Volts Amps Watts explained | Watts vs Volts vs Amps | Amps volts watts explained
Summary
TLDRThis video explains key electrical concepts using a simple syringe analogy. It breaks down voltage, current, resistance, and power in a way that's easy to understand. Voltage is likened to the pressure in a syringe, pushing electric charges through a conductor, while current is the flow rate of these charges. Resistance restricts this flow, and power measures the work done by electricity. The video also covers how appliances' wattage and voltage affect electricity consumption, helping viewers understand how to manage energy use and reduce bills by making informed appliance choices.
Takeaways
- 😀 Voltage is like the pressure in a syringe, pushing electric charges through a conductor.
- 😀 Electric current is the flow of charges through a conductor, measured in amperes (amps).
- 😀 The resistance of a material is similar to the size of a pipe, with thicker conductors offering less resistance and allowing more current to flow.
- 😀 Resistance is measured in ohms, and a material with 1 ohm of resistance requires 1 volt to push 1 ampere of current.
- 😀 Electrical power is measured in watts and depends on both voltage and current.
- 😀 Power consumption in electrical devices is related to how much energy they use per second (measured in watts).
- 😀 Voltage (V) is the electrical energy provided to each charge, while wattage (W) is the energy consumed by the device.
- 😀 Understanding voltage, current, resistance, and power can help you make informed decisions when selecting appliances.
- 😀 Electrical devices like an iron consume more power (watts) due to lower resistance, while devices like light bulbs consume less power.
- 😀 Your electricity bill is based on total energy consumption, measured in kilowatt hours, and understanding wattage helps estimate consumption.
- 😀 To manage electricity bills, it's essential to know how long appliances are used and their wattage to track energy consumption.
Q & A
What is voltage in an electrical circuit?
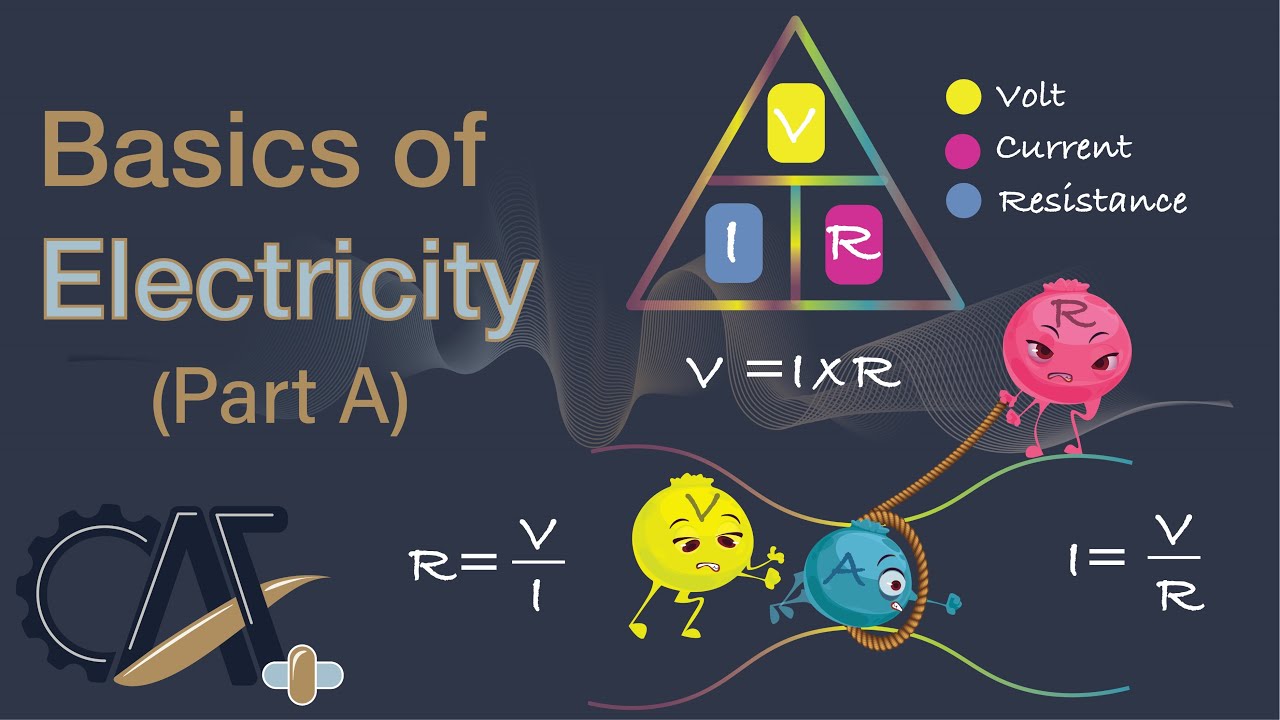
-Voltage is the electrical pressure that pushes electric charges through a conductor in an electrical circuit. It's measured in volts, and higher voltage means stronger electrical pressure and a faster flow of charges.
How does the syringe analogy help explain voltage?
-In the syringe analogy, the pressure you apply to the plunger represents voltage. The harder you push, the greater the pressure, which causes the fluid to flow faster. Similarly, in an electrical circuit, the higher the voltage, the stronger the electrical pressure and the faster the current flows.
What is electric current and how is it measured?
-Electric current is the flow of electric charges through a conductor, similar to the flow rate of a fluid through a pipe. It is measured in amperes (amps). One ampere means one unit of charge flows through the conductor in one second.
How does resistance affect electric current?
-Resistance opposes the flow of electric current. It is measured in ohms. A conductor with higher resistance allows less current to flow, while a conductor with lower resistance allows more current to pass through.
What is the relationship between resistance and the size of a conductor?
-The size of a conductor influences its resistance. A thicker conductor has less resistance, similar to a wider pipe allowing more fluid to flow. A thinner conductor has higher resistance, like a narrow pipe that restricts the flow.
What does it mean when a material has a resistance of 1 ohm?
-A material with a resistance of 1 ohm means that it requires 1 volt of electrical pressure to allow 1 ampere of current to flow through it.
What is power in the context of electricity?
-Power, measured in watts, is the rate at which electrical energy is used or converted into other forms of energy, like heat or light. It depends on both the voltage and the amount of current flowing through a device.
How is power related to voltage and current?
-Power is directly related to both voltage and current. The higher the voltage (pressure) or the current (flow of charges), the greater the power consumed or produced by a device. It’s calculated by multiplying voltage and current.
What is the significance of kilowatt-hours (kWh) on your electricity bill?
-Kilowatt-hours (kWh) represent the total energy consumption of devices over time. 1 kWh equals the energy consumed by a 1,000-watt device running for one hour. This measurement is what contributes to your electricity bill.
Why do appliances like irons consume more electricity than light bulbs?
-Irons have lower resistance than light bulbs, allowing more current to flow through them. This higher current flow results in higher power consumption, which is why irons typically consume around 1,000 watts of power, compared to a light bulb’s 15 watts.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Konsep dasar kelistrikan
Basics of Electricity-Part A [Voltage, Current, Resistance, and Ohm's Law]

Threat, Vulnerability & Risk | A unique way to Understand & Remember the difference | Cybersec Live

W2_L1_Introduction to "Voltage"
IPA Kelas 9 : Listrik Statis IV (Potensial Listrik dan Energi Listrik)

Physics Waves: Frequency & Wavelength FREE Science Lesson
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)